The concepts of the atomic theory were first proposed by the scientist John Dalton. The atomic theory proposed by him explained several aspects of matter in the observable world such as why the pure gold necklace is different from a silver necklace and what happens to a necklace when pure copper is mixed with pure gold. According to Dalton’s theory, all substances are made up of atoms. For chemistry students, understanding atomic structure will help in unravelling the composition and reaction of different elements that they will work with. Atomic theory forms the foundation for studying matter and the universe.
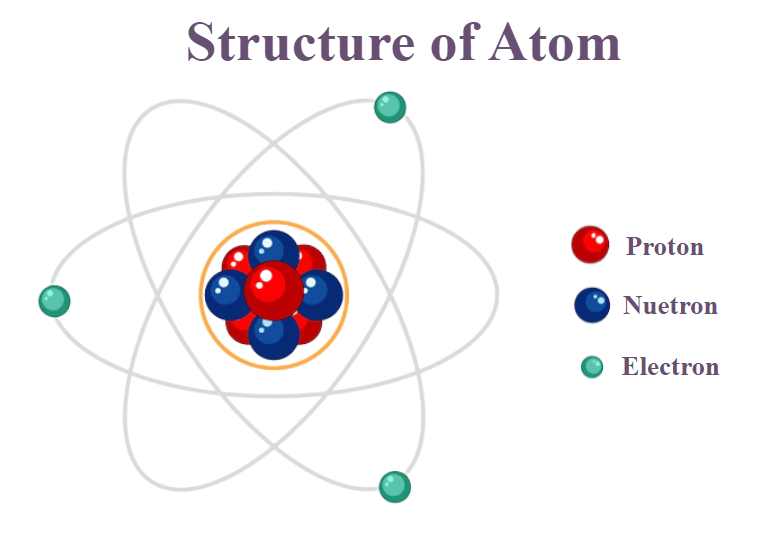
An atom is the smallest piece of an element that maintains the identity of that element. Their size is so small, that it would take around fifty million atoms to make a 1cm long line. The following postulates about atoms form the basis of chemistry.
The word ‘atom’ is derived from the Greek adjective atomos, which means indivisible. However, we now know that atoms can be divided into subatomic particles which include
All atoms of all elements are composed of electrons, protons and neutrons (with one exception).
| Name | Symbol | Mass (approx. in kg) | Charge |
| Electron | e− | 9.1 × 10−31 | 1− |
| Proton | p+ | 1.6 × 10−27 | 1+ |
| Neutron | n, n0 | 1.6 × 10−27 | none |
The subatomic particles aren’t arranged randomly in an atom but follow what is described as a ‘nuclear model’ by the scientist Ernest Rutherford. As per the Rutherford model, the relatively larger protons and neutrons collect in the centre of an atom in a region called the nucleus of the atom. The electrons are outside the nucleus and orbit the space about the nucleus
To understand the Rutherford model, if we blow up an atom to the size of a professional football stadium, that is 105 by 68 metres, then the nucleus would be about the size of a small marble.
Later, Niels Bohr, in Bohr’s model postulated that the electrons could only orbit the nucleus in certain special orbits at different energy levels around the nucleus.

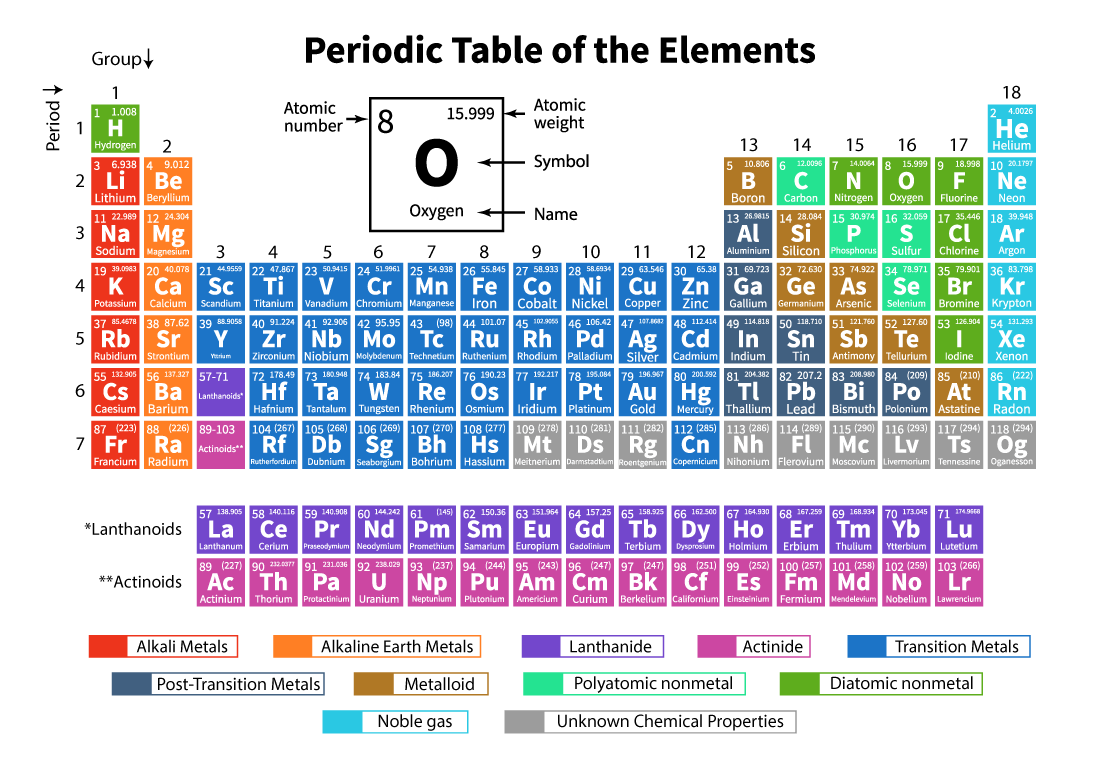
Dmitri Mendeleev, a Russian chemist, suggested that chemical elements exhibited a "periodicity of properties” and tried to organise the chemicals according to their atomic weights. The modern periodic table borrows from Mendeleev’s periodic table structure, however, instead of being organised by atomic weight, the modern table is arranged by atomic number (z). The periodic table rows are called periods and columns are called groups. As we move from left to right in a given period, the chemical properties of the elements change slowly. And elements in a group share many similar chemical and physical properties.
The atomic theory describes the composition of the atom, the properties of the subatomic particles and their behaviour. It forms the foundation for all physics and chemistry. It helps in understanding the periodic table of chemical elements, its structure and its importance in chemistry. It helps us understand and predict the nature of compounds formed by different atoms. It plays an important role in learning nuclear physics, chemistry, pharmacy, astrophysics and more.

© Knowledgeum
