The ongoing debacle at Wayanad district of Kerala where landslides are taking a toll on human life and nature. In Karnataka, there have been 46 landslides this year, with some districts on perpetual red alert and schools being shut down for weeks. What is this phenomenon that causes the mud and rocks to become loose and entire mountains collapsing in a big pile of mush? Let us explore landslides - what they are, what causes them and what can we do to stem their destructive tide.
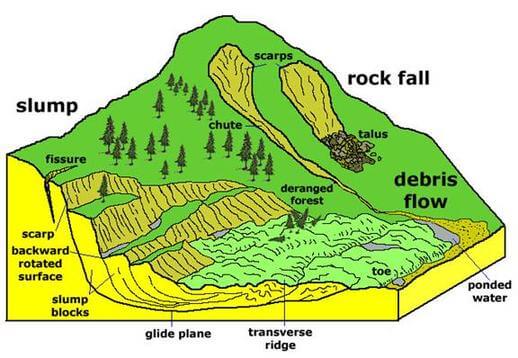
A landslide is defined as the movement of debris, rocks, or earth down a slope. It occurs due to the down-slope movement of soil and rock due to the influence of gravity. The geological materials that flow during a landslide are commonly referred to as mudflows or mudslides. Landslides occur due to man-made or natural factors. They can occur underwater too, which causes earthquakes and other seismic disturbances. Tsunamis are caused by submarine landslides. Landslides are most likely to occur in locations with steep slopes.
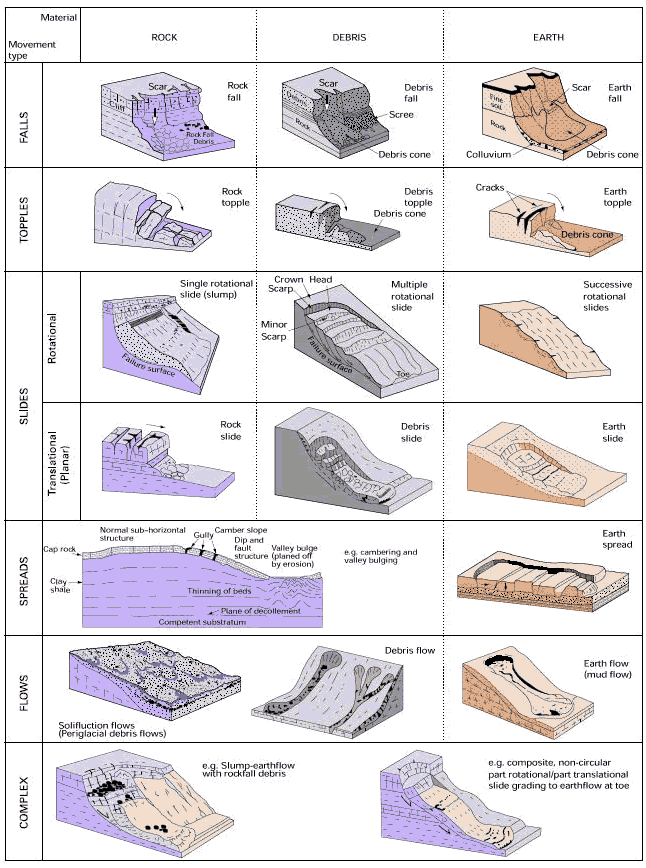
Broadly, landslides are classified by the type of movement that causes them. There are different types of landslides named for the movements that occur during a landslide -

These are sudden movements in the loads of soil, rock and debris that break from the slopes and cliffs. It occurs due to shifts in gravity, earthquakes or mechanical weathering that causes the material to collapse from the slope, fall downwards, and collect towards the base.

The movement of huge masses of rocks, earth and debris from a slope in a forward spin is called topple.

Due to some mass movement, a mass of geological material will break away from the underlying stable material and slide down the slope. The overhead material slides downwards along a slip surface called ‘rupture’. The slide landslide can either be rotational or translational.

When a landslide occurs along the surface of a joint, fault or bedding plane, it is said to be planar or translational. It is highly destructive because the translational landslide causes rapid material movement down a slope. The speed of the slide depends on the depth of the underlying fault.
it can be seasonal, continuous, and progressive and further categorised as
When the surface of the rupture has an upward concave curve and the slide movement rotates about the axis that is parallel to the ground surface and transverse across the slide, it is called a rotational landslide. Rotational landslides occur in regions where resistant rocks founder over underlying weaker rocks. Multiple failures may produce an entire mountainside collapse. These were witnessed in Trotternish on the Isle of Skye, Scotland.
Block Slide is a type of Translational landslide or mudslide that occurs along gently sloping and discrete shear planes with fine-grained rocks. It occurs when the displaced mass becomes viscous due to an increase in pore water pressure. When the overlying material moves as a single deformed mass it is called a block slide.
As evidenced by its name, rock fall occurs when rock or earth falls, rolls or bounces off a cliff, or down a steep slope. Rockfalls start from high outcrops or erosion-resistant, hard rock that becomes unstable due to various reasons. The area’s geology such as bedding thickness, bedding dip and direction, and fracture orientation will determine the size of the falling rock. The speed and intensity of the rock fall are determined by the weathering, position and steepness of the slope. An individual rockfall will only have a few rocks of sizes varying from gravel to large boulders. Then a large mass of rock falls, and the resultant falls spread into a debris fan which is called a debris avalanche.
Landslides occur due to the following factors.
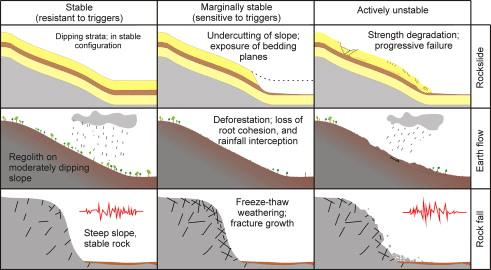
The natural causes of landslides are snowmelt, stream erosion, changes in groundwater level, rainfall, earthquakes and seismic activities, heavy rainfall, soil erosion, volcanic activity or any combination of these factors. Weakly cemented rocks, indurated rocks with prominent or pervasive discontinuities, colluvial or residual land, volcanic soil that contains sensitive clay, granular alluvium and deltaic deposits are common factors for landslides caused by earthquakes.
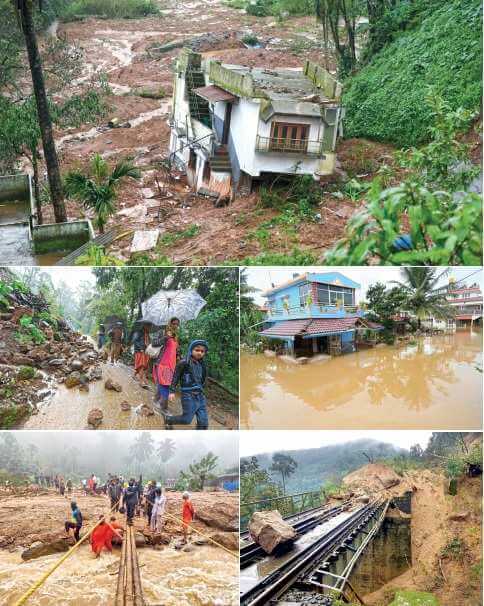

The rise in coffee and tea plantations in the valleys of Kodagu in Karnataka and parts of Kerala are widely speculated causes of monsoon-induced landslides in these regions. Some other human activities that cause landslides are poor environmental impact studies while undergoing construction activities such as building roads and bridges, or buildings in mountain regions. Some human activities that can be considered as the direct causes for landslide-related debacles in recent history are -
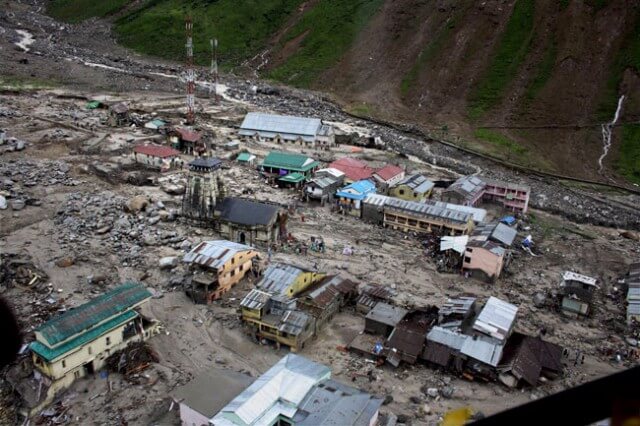

The Kedarnath floods and landslides were caused majorly by over-tourism that led to the mass construction of hotels and tourist spaces, wanton tree-felling and development activity with complete disregard for natural boundaries.

The landslide in Manipur in 2022 spanked an ecological debate. The event that occurred in the seismically active area of western Manipur was linked to climate change and as per the Geological Survey of India report, “extensive slope cut for the construction of the railway station, presence of a break in slope in the upslope area, affluence convergence of water and unprotected slope cut for long duration (from 2014 onwards).”
Deforestation occurs due to poor land management practices caused when -

Construction activities such as building houses, buildings, roads or bridges, and mining space without proper environmental impact study. Mountain areas are tricky, especially because most of them are created due to volcanic or seismic activities. Trees with long and widespread roots play a big role in fastening and binding the rocks and soil. Uprooting them and digging the ground for laying foundations for buildings can prove to be risky as the soil, rock and debris lose their compactness.
In China’s Shenzhen province, the landslide that occurred in December 2015 was partly caused by the soil that was loosened by two years of digging for construction work.
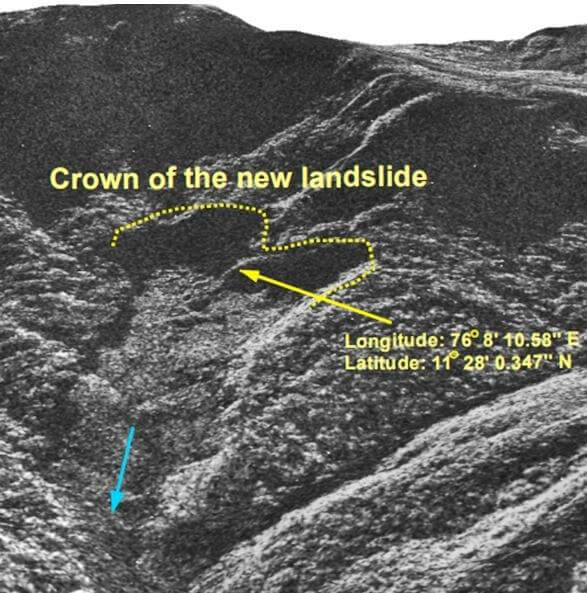
The two massive landslides that occurred in Wayanad in July 2024 at Mundakkal and Chooralmala have wreaked havoc that the region will reel under for the long term. The death toll has reached over 300 and continues to rise and the entire region is facing constant floods with entire buildings, trees and other structures being swept away. The military troops have been deployed to speed up the rescue operations and begin the rehabilitation process. ISRO released satellite images that show that 86,000 metres of land had slipped out of place. The NSRC also found evidence of previous landslides in the same region. They stated that a major flow of debris was triggered in and around Chooralmala.
Wayanad is a sensitive region due to its hilly terrain and high rainfalls. The region had a devastating landslide in 2020 too. Around 50% of Kerala is on slopes of more than 20o and has loose topsoil. As per India Today report, “In July 2022, the Ministry of Earth Sciences informed the Lok Sabha that Kerala had seen the highest number of major landslides in the country over the past seven years. Of the 3,782 landslides recorded between 2015 and 2022, approximately 59.2%, or 2,239, occurred in God's Own Country.”

In the same article, Kerala-based disaster expert, S. Sreekumar was quoted saying, "A lot of construction activities are happening in vulnerable areas of Kerala. Even now, our engineering structures are being built based on the amount of rainfall and intensity of rainfall in older days. There is a need to rethink new or added risk factors while constructing roads or culverts. Our unscientific construction mechanisms are major causes of the destruction we are facing."
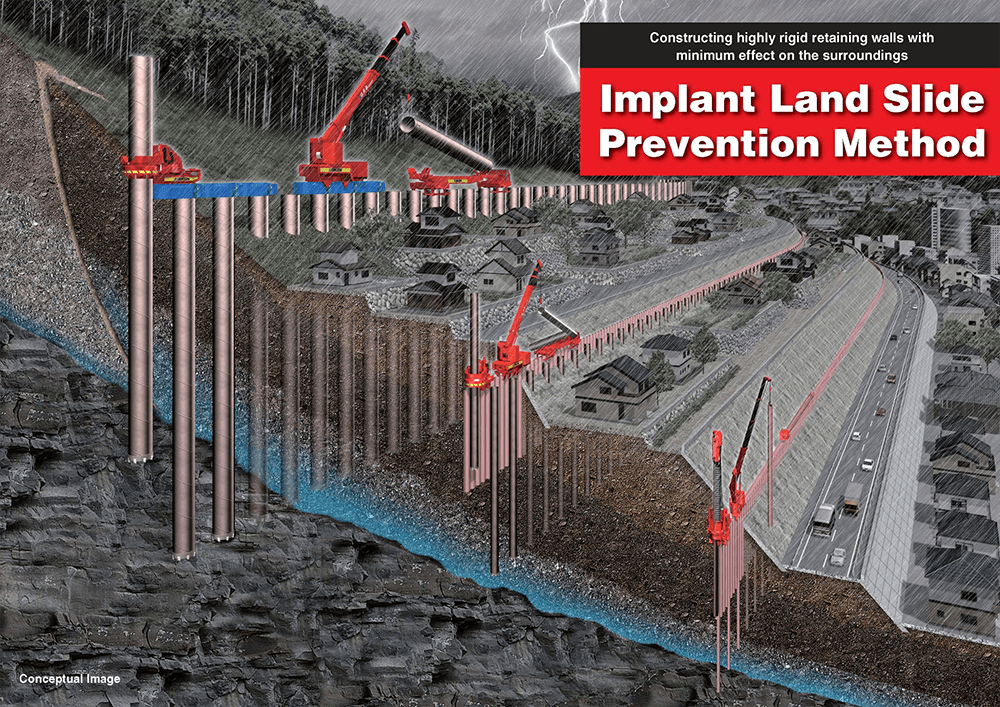
While we cannot control the environmental factors that cause landslides, a collective effort from individuals, government and institutions can be taken towards controlling the man-made causes of landslides. Some of these are -
After a landslide occurs, stabilisation projects must be undertaken and implemented rapidly to prevent further damage and restore affected areas. A detailed investigation with transparent reporting must be done to study the causes of landslides and improve future prevention and response strategies.
© Knowledgeum
